Evaluating Weaviate Query Agents¶
The Weaviate Query Agent is a pre-built agentic service designed to answer natural language queries based on the data stored in Weaviate Cloud.
The user simply provides a prompt/question in natural language, and the Query Agent takes care of all intervening steps to provide an answer.
To evaluate a Weaviate Query agent, we can access metadata from the intermediate steps in the response object for evaluation. Then, we can use this metadata to evaluate things like the relevance of the filter used by the query agent.
Custom evaluations are particularly valuable here, because they allow us to easily extend existing evaluations to unique scenarios. In this example, we show how to record a Query Agent run. We also show how to use custom instructions to customize an existing LLM judge to provide tailored feedback for our situation.
By evaluating this ecommerce agent, we are able to identify opportunities for improvement when the search results include items that do not match what the customer is looking for.
See this example as a Weaviate recipe!
Follow along!
Setup¶
import os
os.environ["TRULENS_OTEL_TRACING"] = "0"
#! pip install trulens-core trulens-providers-openai trulens-dashboard weaviate-client weaviate-agents datasets pydantic==2.10.6 # note: pydantic < 2.11.0 is required for now due to compatibility issue
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-proj-..."
os.environ["WEAVIATE_URL"]="..."
os.environ["WEAVIATE_API_KEY"]="..."
os.environ["HUGGINGFACE_API_KEY"]="hf_..."
Create weaviate client¶
import weaviate
from weaviate.classes.init import Auth
from weaviate.agents.query import QueryAgent
headers = {
# Provide your required API key(s), e.g. Cohere, OpenAI, etc. for the configured vectorizer(s)
"X-HuggingFace-Api-Key": os.environ["HUGGINGFACE_API_KEY"],
}
client = weaviate.connect_to_weaviate_cloud(
cluster_url=os.environ["WEAVIATE_URL"],
auth_credentials=Auth.api_key(os.environ["WEAVIATE_API_KEY"]),
headers=headers,
)
Load data¶
from weaviate.classes.config import Configure, Property, DataType
# Using `auto-schema` to infer the data schema during import
client.collections.create(
"Brands",
description="A dataset that lists information about clothing brands, their parent companies, average rating and more.",
vectorizer_config=Configure.Vectorizer.text2vec_weaviate(),
)
# Explicitly defining the data schema
client.collections.create(
"ECommerce",
description="A dataset that lists clothing items, their brands, prices, and more.",
vectorizer_config=Configure.Vectorizer.text2vec_weaviate(),
properties=[
Property(name="collection", data_type=DataType.TEXT),
Property(
name="category",
data_type=DataType.TEXT,
description="The category to which the clothing item belongs",
),
Property(
name="tags",
data_type=DataType.TEXT_ARRAY,
description="The tags that are assocciated with the clothing item",
),
Property(name="subcategory", data_type=DataType.TEXT),
Property(name="name", data_type=DataType.TEXT),
Property(
name="description",
data_type=DataType.TEXT,
description="A detailed description of the clothing item",
),
Property(
name="brand",
data_type=DataType.TEXT,
description="The brand of the clothing item",
),
Property(name="product_id", data_type=DataType.UUID),
Property(
name="colors",
data_type=DataType.TEXT_ARRAY,
description="The colors on the clothing item",
),
Property(name="reviews", data_type=DataType.TEXT_ARRAY),
Property(name="image_url", data_type=DataType.TEXT),
Property(
name="price",
data_type=DataType.NUMBER,
description="The price of the clothing item in USD",
),
],
)
from datasets import load_dataset
brands_dataset = load_dataset(
"weaviate/agents", "query-agent-brands", split="train", streaming=True
)
ecommerce_dataset = load_dataset(
"weaviate/agents", "query-agent-ecommerce", split="train", streaming=True
)
brands_collection = client.collections.get("Brands")
ecommerce_collection = client.collections.get("ECommerce")
with brands_collection.batch.dynamic() as batch:
for item in brands_dataset:
batch.add_object(properties=item["properties"], vector=item["vector"])
with ecommerce_collection.batch.dynamic() as batch:
for item in ecommerce_dataset:
batch.add_object(properties=item["properties"], vector=item["vector"])
failed_objects = brands_collection.batch.failed_objects
if failed_objects:
print(f"Number of failed imports: {len(failed_objects)}")
print(f"First failed object: {failed_objects[0]}")
print(f"Size of the ECommerce dataset: {len(ecommerce_collection)}")
print(f"Size of the Brands dataset: {len(brands_collection)}")
Create the Query Agent¶
from weaviate.agents.query import QueryAgent
from trulens.apps.app import instrument
class Agent:
def __init__(self, client):
self.agent = QueryAgent(
client=client,
collections=["ECommerce", "Brands"],
)
@instrument
def run(self, query):
return self.agent.run(query)
@instrument
def fetch_sources(self, agent_response): # fetch sources is unneccessary, but gives us more power to examine and evaluate the sources
sources = []
for source in agent_response.sources:
object_id = source.object_id
collection_name = source.collection
collection = client.collections.get(collection_name)
data_obj = collection.query.fetch_object_by_id(object_id)
sources.append(data_obj)
return sources
@instrument
def run_and_fetch_sources(self, query):
agent_response = self.run(query)
self.fetch_sources(agent_response)
return agent_response
query_agent = Agent(client)
Create feedback functions¶
from trulens.providers.openai import OpenAI as fOpenAI
from trulens.core import Feedback
from trulens.core import TruSession
from trulens.core import Select
session = TruSession()
session.reset_database()
# Initialize OpenAI-based feedback function collection class:
fopenai = fOpenAI()
custom_criteria = "You are specifically gauging the relevance of the filter, described as a python list of dictionaries, to the query. The filter is a list of dictionaries, where each dictionary represents a filter condition. Each dictionary has three keys: 'operator', 'property_name', and 'value'. The 'operator' key is a string that represents the comparison operator to use for the filter condition. The 'property_name' key is a string that represents the property of the object to filter on. The 'value' key is a float that represents the value to compare the property to. The relevance score should be a float between 0 and 1, where 0 means the filter is not relevant to the query, and 1 means the filter is highly relevant to the query."
# Define a relevance function from openai
f_answer_relevance = Feedback(fopenai.relevance, name = "Answer Relevance").on_input().on(Select.RecordCalls.run.rets.final_answer)
f_filter_relevance = Feedback(fopenai.relevance, name = "Filter Relevance",
min_score_val=0,
max_score_val=1,
criteria = custom_criteria,
).on_input().on(Select.RecordCalls.run.rets.searches[0][0].filters[0][0].collect())
f_context_relevance = (
Feedback(fopenai.context_relevance_with_cot_reasons,
name = "Context Relevance",
criteria="Evaluate the relevance of the individual SEARCH RESULT option to the query, regardless of whether the user requests multiple options. If the only issue is that the SEARCH RESULT does not provide a list of multiple options, return a RELEVANCE score of 3.")
.on_input()
.on(Select.RecordCalls.fetch_sources.rets[:].properties)
)
Register the agent¶
from trulens.apps.app import TruApp
tru_agent = TruApp(
query_agent,
app_name="query agent",
app_version="base",
feedbacks=[f_answer_relevance, f_filter_relevance, f_context_relevance],
)
Run and record the agent¶
with tru_agent as recording:
response = query_agent.run_and_fetch_sources("I like vintage clothes, can you list me some options that are less than $200?")
Run the dashboard¶
from trulens.dashboard import run_dashboard
run_dashboard(session) # open a local streamlit app to explore
Identify issue using the TruLens dashboard¶
By evaluating the query agent, we notice it occasionally returns non-clothing items even though the customer specifically asks for clothing.
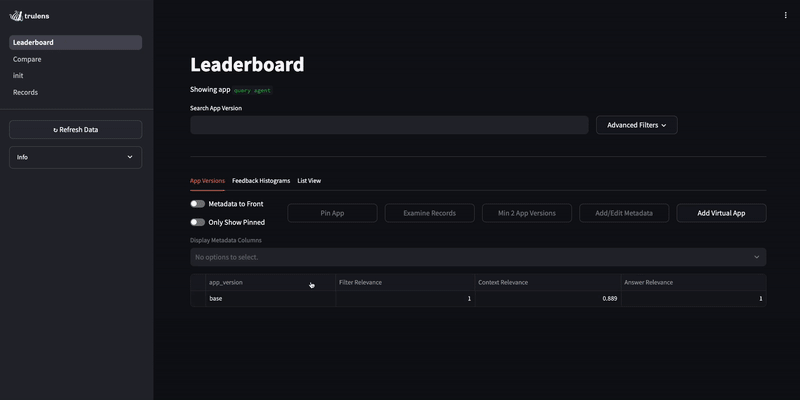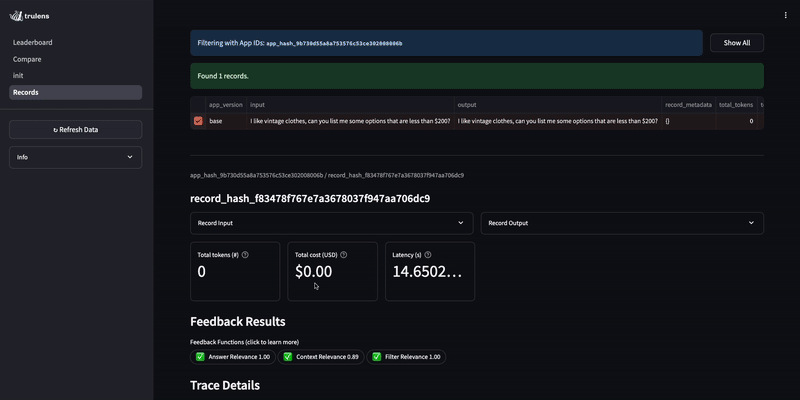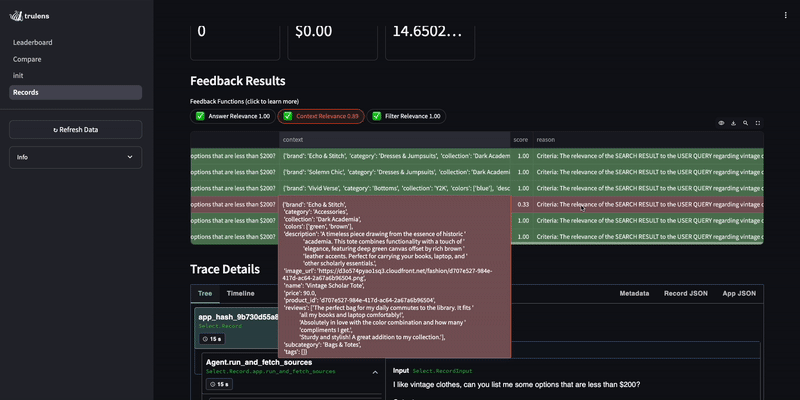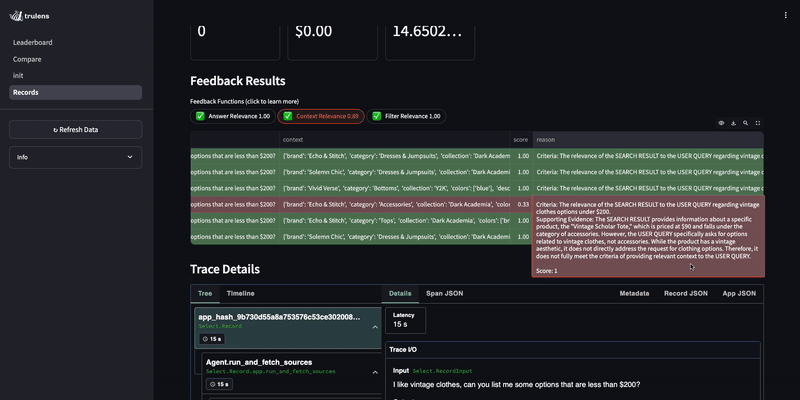
Improve the agent¶
Let's add additional instruction into the system prompt to help guide the agent to return only the type of result the user is looking for.
from weaviate.agents.query import QueryAgent
from trulens.apps.app import instrument
class Agent:
def __init__(self, client):
self.agent = QueryAgent(
client=client,
collections=["ECommerce", "Brands"],
system_prompt="You are a helpful assistant that always returns only results that match the user's query. For example, if the user asks for clothing, only return clothing."
)
@instrument
def run(self, query):
return self.agent.run(query)
@instrument
def fetch_sources(self, agent_response): # fetch sources is unneccessary for running the agent, but gives us more power to examine and evaluate the sources
sources = []
for source in agent_response.sources:
object_id = source.object_id
collection_name = source.collection
collection = client.collections.get(collection_name)
data_obj = collection.query.fetch_object_by_id(object_id)
sources.append(data_obj)
return sources
@instrument
def run_and_fetch_sources(self, query):
agent_response = self.run(query)
self.fetch_sources(agent_response)
return agent_response
query_agent = Agent(client)
Validate performance¶
Last, we'll register the improved version of the app and validate the performance improvement
from trulens.apps.app import TruApp
tru_agent = TruApp(
query_agent,
app_name="query agent",
app_version="modified system prompt",
feedbacks=[f_answer_relevance, f_filter_relevance, f_context_relevance],
)
with tru_agent as recording:
response = query_agent.run_and_fetch_sources("I like vintage clothes, can you list me some options that are less than $200?")
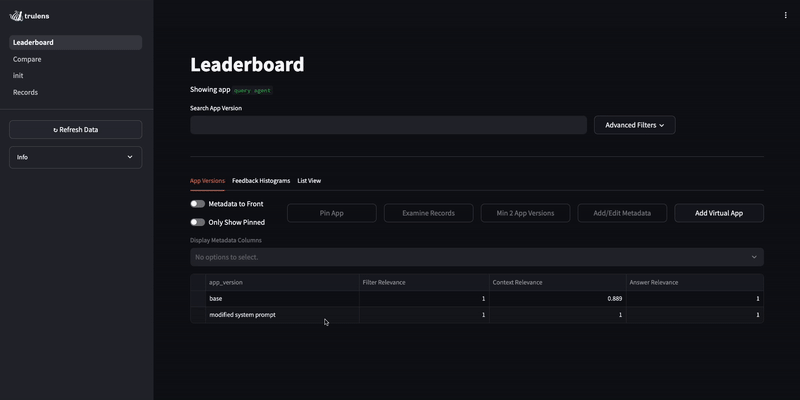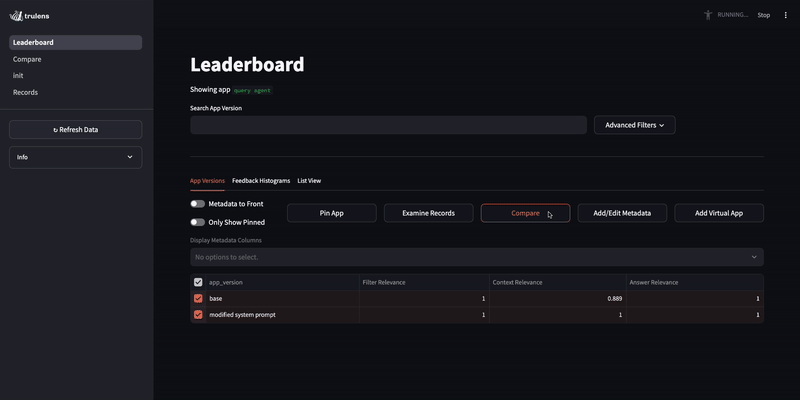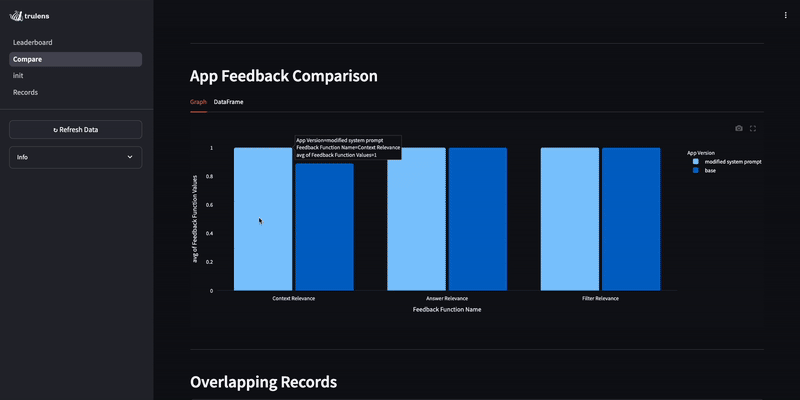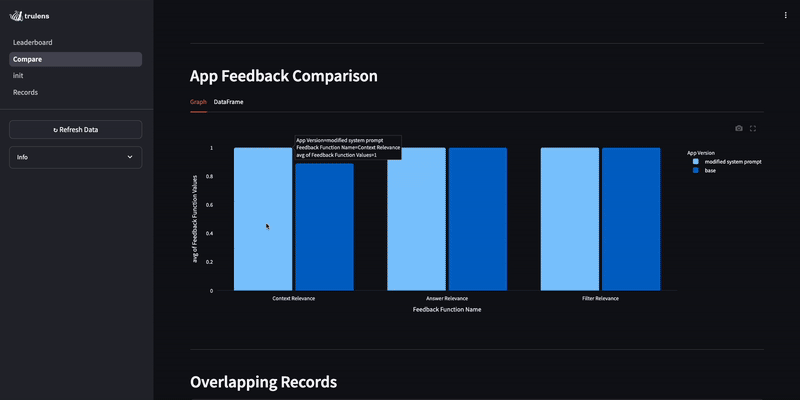
In the dashboard, we can compare application versions and their evaluation results.
Comparing here, we see the context relevance improvement.